Trees, Shrubs and Woody Vines
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Alnus glutinosa
Description
Native to Europe and Asia, European, or black alder is planted widely as an ornamental. In some parts of the United States and elsewhere in the world, this species becomes weedy, even invasive. In Missouri, you are most likely to encounter it in landscaped areas, and not in the wild.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Lonicera flava
Description
One of our beautiful, native Missouri honeysuckles, yellow honeysuckle grows mainly in the Ozarks. Unlike the invasive Japanese honeysuckle, this plant is not aggressive and makes a wonderful trellis vine for the ecology-minded gardener.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Lonicera dioica
Description
Limber honeysuckle is a native Missourian. It's uncommon and widely scattered in the state, but it does well as a trellis vine. Identify it by its crowded clusters of tubular, yellow or greenish-yellow flowers, tinged with red, purple, or pink, that are noticeably enlarged on one side at the base.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Lonicera reticulata (formerly L. prolifera)
Description
One of Missouri's beautiful native honeysuckles, grape honeysuckle is found mainly in the northern two-thirds of the state. In the native plant garden, it is easy to grow, but it is not aggressive like the introduced invasive Japanese honeysuckle.
Media
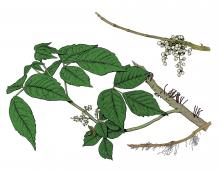
Species Types
Scientific Name
Toxicodendron radicans
Description
Poison ivy is a toxic plant that contains an oil in all its parts that, if you come into contact with it, can cause an intense skin reaction. Learn to recognize it, and sidestep it on your outings.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Fraxinus spp.
Description
Missouri has six species of ashes that you might find in natural settings. They have been very popular as shade trees, and their wood is famously useful. Ash trees of all the species in North America are currently being killed by the invasive, nonnative emerald ash borer.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Vaccinium stamineum
Description
Deerberry is an irregularly branched shrub, rarely more than 6 feet high. A blueberry relative, it bears edible blue fruits.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Vaccinium pallidum (syn. V. vacillans)
Description
Lowbush blueberry is a stiffly branching shrub to 3 feet high. The berries are tasty raw or cooked in pies, muffins, and preserves. It is mostly found south of the Missouri River. It often grows in extensive colonies.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Vaccinium arboreum
Description
Farkleberry, or sparkleberry, is a stiff-branched shrub or small crooked tree growing in loose thickets on rocky soils, mostly south of the Missouri River. A type of blueberry, its black fruits are edible but dry and mealy.
Media

Species Types
Scientific Name
Aristolochia tomentosa
Description
Woolly pipe-vine is a high-climbing woody vine common along streams in the Ozarks. Hikers and canoeists often don’t notice it because the leaves and unusual flowers are usually high overhead in the trees.
See Also
About Trees, Shrubs and Woody Vines in Missouri
There are no sharp dividing lines between trees, shrubs, and woody vines, or even between woody and nonwoody plants. “Wood” is a type of tissue made of cellulose and lignin that many plants develop as they mature — whether they are “woody” or not. Trees are woody plants over 13 feet tall with a single trunk. Shrubs are less than 13 feet tall, with multiple stems. Vines require support or else sprawl over the ground.





















